Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
We analyzed a total sample of 52,361 individuals sequenced with Illumina technology. Of these, 24,510 individuals (18,403 after QC) were collected as part of the Alzheimer Disease European Sequencing consortium (ADES), comprising 15 studies from Germany, France, The Netherlands, Spain, Italy, and the United Kingdom. All studies were approved by the ethics committees of respective institutes, and all participants provided informed consent for study participation. These samples were combined with 27,851 samples from the USA (14,155 after QC), the majority of which were from the Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project (ADSP).
We are currently working on a new data release, using the newest variant calling algorithms. This release is expected to be released in 2024, and will be at least twice as large as release 1.
Across all studies, AD cases were defined according to NIAA criteria for possible or probable AD or according to NINCDS-ADRDA criteria depending on the date of diagnosis. When possible, supportive evidence for an AD pathophysiological process was sought (including CSF biomarkers) or the diagnosis was confirmed by neuropathological examination. Cases were annotated with the age at onset or age at diagnosis, otherwise, samples were classified as late onset AD. Controls were not diagnosed with AD. All contributing datasets were sequenced using a paired-end Illumina platform, but different exome capture kits were used, and a subset of the sample was sequenced using whole genome sequencing.
The ADES-FR project combines WES and WGS data from AD cases and controls from France. Unrelated cases with early-onset AD from France were recruited among patients who fulfilled the NIAA criteria. The clinical examination included personal medical and family history assessment, neurologic examination, neuropsychological assessment, and neuroimaging. In addition, CSF biomarkers indicative of AD were available for 67% of the cases. Patients were either screened by Sanger sequencing and QMPSF for pathogenic variants in APP, PSEN1 or PSEN2 prior to WES or by the interpretation of WES data or both.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

The AgeCoDe-UKBonn sample was derived from the German study on Aging, Cognition and Dementia in primary case patients and the interdisciplinary Memory Clinic at the University Hospital of Bonn. The AgeCoDe study aims to identify risk factors and predictors of cognitive decline and dementia. Participants were recruited from general practitioner registries. Inclusion criteria were an age of 75 and older, absence of dementia, one or more visits to the GP in the past year, no hearing or vision impairments and German as a native language. Exclusion criteria were only home-based GP consultations, severe illness with a fatal outcome within 3 months and a language barrier.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

Neuropathological samples were obtained from the Neurological Tissue Bank of the Biobanc-HospitalClinic-IDIBAPS, and disease evaluation was perfromed according to international consensus criteria. Clinical samples were recruited from the multimodel Sant Pau Initiative on Neurodegeneration cohort, and were evaluated at the Memory Unit at Hospital de Sant Pau (Barcelona). All controls had normal cognitive scores in the formal neuropsychological evaluation and normal core CSF AD biomarkers, based on previously published cut-offs. AD patients fulfilled clinical criteria of 'probable AD dementia with evidence of the AD pathophysiological process and therefore had abnormal core AD biomarkers in the CSF. The SPIN cohort is based on blinded enrollment and only clinically relevant biomarker results are disclosed.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

The Alzheimer Center Erasmus MC cohort includes patient refered to the Department of Neurology of the Erasmus Medical Center. DNA samples from 125 patients with probably AD were included in the current study. The average age at onset was 60 years. A large fraction of the patients had a positive family history, defined as at least one first degree relative with dementia. All patients underwent clinical examination, neuropsychological assessment, neuroimaging, and if indicated, a lumbar puncture. The diagnosis was established according to the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria for AD.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

The Erasmus Ruchphen Family (ERF) Study is a family-based cohort study that is embedded in the Genetic Research in Isolated Populations (GRIP) program in the South West of the Netherlands. The aim of this program was to identify genetic risk factors in the development of complex disorders. For the ERF study, 22 families that had at least five children baptized in the community church between 1850-1900 were identified with the help of genealogical records. All living descendants of these couples and their spouses were invited to take part in the study.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

The Rotterdam Study is an ongoing prospective population-based cohort study, focused on chronic disabling conditions of the elderly of which a random subset was exome sequenced. Participants were screened for dementia at baseline and at follow-up examinations using the MMSE and GMS organic level. Screen-positives underwent extensive examination. Finally, individuals were diagnosed in accordance with standard criteria for dementia and Alzheimer's disease, NINCDS-ARDRA.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

The ADC-Amsterdam cohort includes patients who visit the memory clinic of the Alzheimer Center at the Amsterdam University Medical Center, The Netherlands. DNA samples from 854 patients with probable and possible AD were included in the current study. Additionally, 353 individuals diagnosed with psychiatric and subjective cognitive complaints were included as controls. Individuals in this cohort were extensively characterized to reduce the chance of misdiagnosis. Patients underwent an extensive standardized dementia assessment, including medical history, informant-based history, a physical examination, routine blood and CSF laboratory tests, neuropsychological testing, EEG and MRI of the brain.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

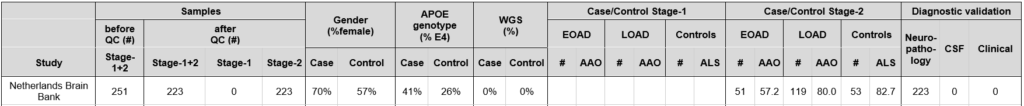
From the Netherlands Brain Bank, we selected brain tissues donated by patients diagnosed with Alzheimer Disease. DNA was isolated and used for WES sequencing.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in
This cohort consists of WES data that were generated as part of a diagnostic work-up. All samples are from healthy adults for whom WES analysis was performed to aid the analysis of a patient, in most cases these were healthy parents of an affected child for whom trio-WES analysis was performed. These parents either have no pathogenic variant, or are carrier of one recessive pathogenic variant that does not affect health.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

The 100-plus Study, is a prospective cohort study of cognitively healthy centenarians that associated with the Alzheimer Center at the Amsterdam University Medical Center. Trained researchers visited the centenarians at their home residence annually, where they were subjected to questionnaires regarding demographics, lifestyle, medical history, physical well-being and objective measurements of cognitive and physical functions. Cognitive function is tested by an extensive neuropsychological testing battery. For the current stuy, DNA samples of 375 centenarians were included who completed at least one neuropsychological test at baseline, and exome sequencing from 349 centenarians passed QC.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

The EMIF-AD 90+ study22 is a cohort-study of the oldest-old (90+), situated at the Amsterdam UMC and the University of Manchester. The study contributed n=72 controls. Controls were tested to have a Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) >=26 and a global Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) score of 0 at baseline.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

The Control Brain Consortium consists of whole-exome sequencing in 478 samples derived from several brain banks in the United Kingdom and the United States of America. Samples were included when subjects were, at death, over 60 years of age, had no signs of neurological disease and were subjected to a neuropathological examination, which revealed no evidence of neurodegeneration.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

The PERADES sample comprises individuals with Alzheimer's disease and healthy controls recruited across UK, Italy and Spain. The participants were assessed at home or in research clinics along with an informant, usually a spouse, family member or close friend, who provided information about and on behalf of the individual with dementia. Established measures were used to ascertain the disease severity. Control participants were recruited from GP surgeries and by means of self-referral. For all other recruitment, all AD cases met criteria for either probable or definite AD. Control samples were chosen to match case samples for age, gender, ethnicity and country of origin.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

University College London Dementia Research Centre early-onset Alzheimer's disease cohort included patients seen at the Cognitive Disorders Clinics at The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, or affiliated hospitals. Individuals were assessed clinically and diagnosed as having probably Alzheimer's disease based on contemporary clinical criteria in use at the time, including imaging and neuropsychological testing where approporiate. All individuals consented for genetic testing and had causative mutations for Alzheimer's disease and prion disease excluded prior to entry into this study.
Website: to be filled in
Contact person: to be filled in

ADSP Discovery phase: Cases and controls were selected from over 30,000 non-Hispanic Caucasian subjects from multiple cohorts. All controls were greater than 60 years and were cognitively normal based on direct assessment. All cases met NINCDS-ADRDA criteria for possible, probably, or definite Alzheimer's disease. All cases had documented age-at-onset, and for those with pathologically confromed AD, an age-at death. APOE genotypes were available for all. Cases were selected to have a minimal AD risk based on sex, age and APOE genotype. Controls were selected as those with the least probability of converting to AD by age 85.
ADSP Discovery extension and Augmentation phase: An additional 3,000 subjects were whole genome sequenced.
Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: A publice private partnership, the prupose of ADNI is to develop a multisite, longitudinal, prospective, naturalistic study of normal cognitive aging, mild cognitive impairment, and early Alzheimer's disease as a public domain research resource to facilitate the scientific evaluation of neuroimaging and other biomarkers for the onset and progression of MCI and Alzhiemer's disease.

The overall goals are to identify and characterize novel genetic variants that promote resilience to AD pathology in the presence of the APOE4 allele or that drive pathogenesis in the absence of the APOE4 allele. Genomes are collected from several sources, some intramural and some extramural. Invariably, the cognitive assessment protocols for these different sources vary somewhat but all include APOE genotyping, extensive neuropsychological testing, collection of one or more AD biomarkers, and consensus adjudication.

The samples were recruited at Washington University School of Medicine in Saint louis, MO. All the cases received a diagnosis of dementia of the Alzheimer's type (DAT), using criteria equivalent to the National Institute of Neurological and Communication Disorders and Stroke-Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders Association for probable AD. Cognitively normal participants received the same assessment as the cases, and were deemed nondemented. Prior written consent, participants are genotyped for APOE4 allele and screened for known mutation in APP, PSEN1, PSEN2, MAPT, GRN, or C9orf72 by the Clinical and Genetics Core of the Knight ADRC

Cases were selected from the University of California, San Francisco Memory and Aging Center with an intentional selection of early-onset cases to maximize the likelihood of identifying genetic contributors, along with healthy older adult controls. All UCSF cases and controls were clinically assessed during an in-person visit to the UCSF Memory And Aging Center that included a neurological exam, cognitive assessment, and medical history. Eacht participant's study partner was also interviewed regarding functional abilities. This cohort was intentionally depleted of cases with known Mendelian variants associated with neurodegenerative diseases. A small number of samples were obtained from the University of alabama at Birmingham from an expert clinician who emplyed the same diagnostic procedures.

